In this post we will be talking about SAML based single signon, specifically about a webapp (service provider) initiated single signon.
Single Signon or short SSO allows us to reuse identities for multiple service providers (applications).
The applications do not need to know about the identity information just the identity provider.
There is a trust relationship between the service provider and the identity provider and then the authentication process is as follows. 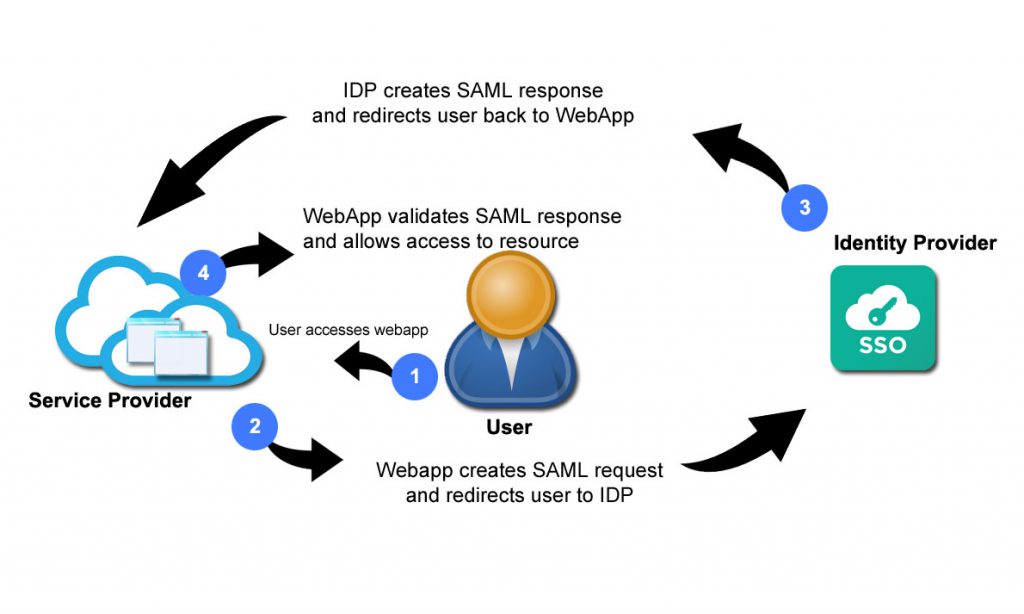
Trust Relationship
As mentioned previously a trust relationship between the identity provider and the service provider must exist. This is done by the exchange of SAML metadata between the two providers
Authentication Process
First the user attempts to access the webapp (resource at the serviceprovider)
In step 2 the service provider creates a SAML request and redirects the user to the identity provider using that request
This SAML request contains information about the service provider and in most cases certificates and public keys
The identity provider will now handle the authentication process. Once the user is authenticated the identity provider will create a SAML response containing information about the users identity and send the user back to the service provider.
The service provider receives the SAML response and will now validate the SAML response to make sure it is a valid response from a valid, trusted identity provider.
Once the validation is complete the service provider allows access to the resource

